Can a Company's Shares Exhibit a Negative P/e Ratio
What is the Price Earnings Ratio?
The Cost Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio) is the relationship between a company's stock cost and earnings per share (EPS) . It is a popular ratio that gives investors a better sense of the value of the company. The P/E ratio shows the expectations of the market and is the cost you lot must pay per unit of current earnings (or future earnings, equally the case may be).
Earnings are important when valuing a company's stock because investors want to know how profitable a company is and howassisting it will be in the time to come. Furthermore, if the company doesn't grow and the current level of earnings remains constant, the P/East can be interpreted equally the number of years it volition have for the visitor to pay back the amount paid for each share.

Image: CFI'due south Financial Analysis Courses .
P/Due east Ratio in Employ
Looking at the P/E of a stock tells you very little about it if it's not compared to the company'south historical P/E or the competitor's P/E from the aforementioned manufacture. It's not easy to conclude whether a stock with a P/Eastward of 10x is a bargain or a P/E of 50x is expensive without performing whatsoever comparisons.
The beauty of the P/E ratio is that it standardizes stocks of different prices and earnings levels.
The P/E is also called an earnings multiple. There are ii types of P/E: abaft and forrad. The former is based on previous periods of earnings per share, while a leading or forrad P/Due east ratio is when EPS calculations are based on futurity estimates, which predicted numbers (frequently provided by management orequity research analysts ).
Price Earnings Ratio Formula
P/E = Stock Cost Per Share / Earnings Per Share
or
P/E = Market Capitalization / Total Cyberspace Earnings
or
Justified P/E = Dividend Payout Ratio / R – G
where;
R = Required Rate of Render
K = Sustainable Growth Rate
P/E Ratio Formula Explanation
The bones P/East formula takes the current stock price and EPS to find the current P/Due east. EPS is found by taking earnings from the final twelve months divided past the weighted average shares outstanding . Earnings can be normalized for unusual or one-off items that tin impact earnings abnormally. Larn more about normalized EPS .
The justified P/E ratio is used to find the P/Due east ratio that an investorshould be paying for, based on the companies dividend and memory policy, growth rate, and the investor'south required rate of render . Comparing justified P/E to basic P/E is a common stock valuation method.
Why Apply the Price Earnings Ratio?
Investors want to buy financially sound companies that offer a practiced render on investment (ROI) . Among the many ratios, the P/Due east is office of the research process for selecting stocks considering nosotros can figure out whether we are paying a fair price.
Similar companies inside the aforementioned manufacture are grouped together for comparison, regardless of the varying stock prices. Moreover, information technology'due south quick and easy to use when we're trying to value a company using earnings. When a high or a low P/Eastward is institute, nosotros can quickly assess what kind of stock or company we are dealing with.
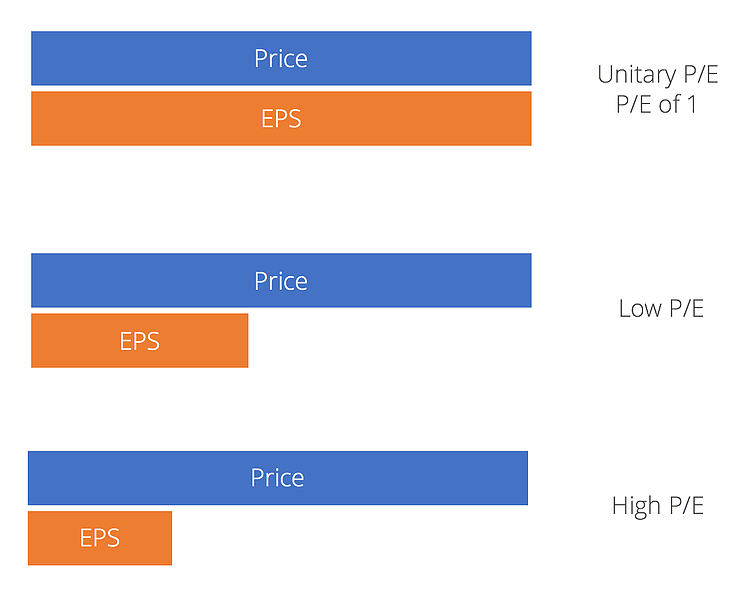
Loftier P/Eastward
Companies with a high Price Earnings Ratio are often considered to be growth stocks. This indicates a positive future performance, and investors have higher expectations for future earnings growth and are willing to pay more than for them.
The downside to this is that growth stocks are often higher in volatility, and this puts a lot of pressure on companies to do more to justify their higher valuation. For this reason, investing in growth stocks volition more likely be seen as a risky investment. Stocks with high P/Due east ratios can also be considered overvalued.
Depression P/East
Companies with a low Price Earnings Ratio are oftentimes considered to exist value stocks. It means they are undervalued because their stock prices trade lower relative to their fundamentals. This mispricing volition be a great bargain and will prompt investors to buy the stock before the market corrects it. And when it does, investors make a profit as a result of a higher stock price. Examples of low P/East stocks can be plant in mature industries that pay a steady rate of dividends .
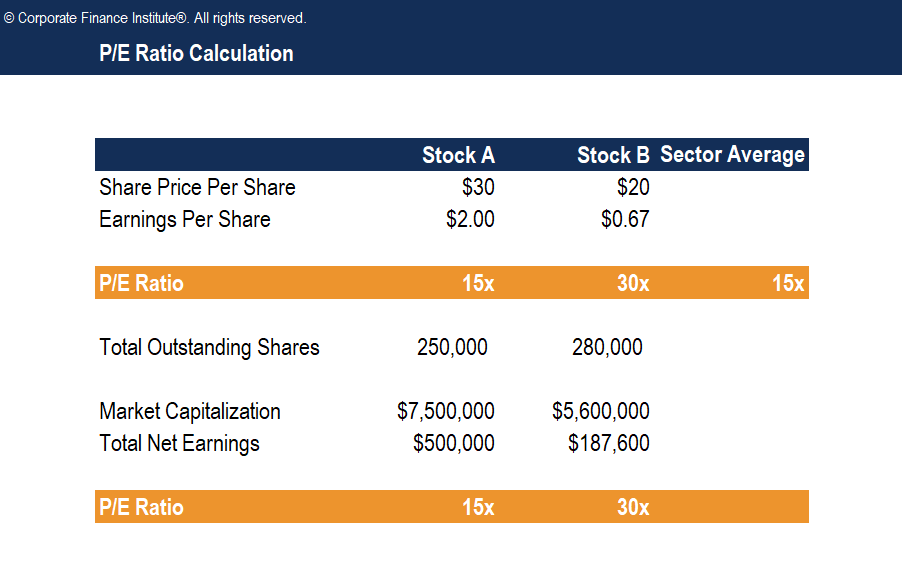
P/Eastward Ratio Example
If Stock A is trading at $xxx and Stock B at $xx, Stock A is non necessarily more expensive. The P/E ratio tin can assistance usa determine, from a valuation perspective, which of the 2 is cheaper.
If the sector's boilerplate P/E is 15, Stock A has a P/E = 15 and Stock B has a P/E = 30, stock A is cheaper despite having a higher absolute cost than Stock B because you pay less for every $1 of current earnings. However, Stock B has a higher ratio than both its competitor and the sector. This might mean that investors will expect higher earnings growth in the futurity relative to the marketplace.
The P/E ratio is but ane of the many valuation measures and fiscal analysis tools that nosotros use to guide us in our investment determination, and it shouldn't be the only ane.
Download the Free Template
Enter your name and electronic mail in the form below and download the free template now!
P/E Ratio Template
Download the complimentary Excel template now to advance your finance knowledge!
Video Explanation of the Price Earnings Ratio
Below is a short video that explains how to calculate a company's price-to-earnings ratio and how to interpret the results.
Video: CFI'southward Financial Assay Courses .
Justified P/E Ratio
The justified P/Eastward ratio above is calculated independently of the standard P/E. In other words, the two ratios should produce two different results. If the P/E is lower than the justified P/E ratio, the company is undervalued, and purchasing the stock will result in profits if the alpha is closed.
Limitations of Price Earnings Ratio
Finding the truthful value of a stock cannot merely be calculated using electric current year earnings. The value depends on all expected future cash flows and earnings of a visitor. Price Earnings Ratio is used as a good starting point. It ways niggling only past itself unless we have some agreement of the growth prospects in EPS and take a chance profile of the company. An investor must dig deeper into the company's financial statements and use other valuation and financial assay methods to get a better film of a company'due south value and performance.
Additionally, the Price Earnings Ratio can produce wonky results, as demonstrated below. Negative EPS resulting from a loss in earnings volition produce a negative P/E. An exceedingly high P/E can exist generated by a visitor with close to zero net income, resulting in a very low EPS in the decimals.
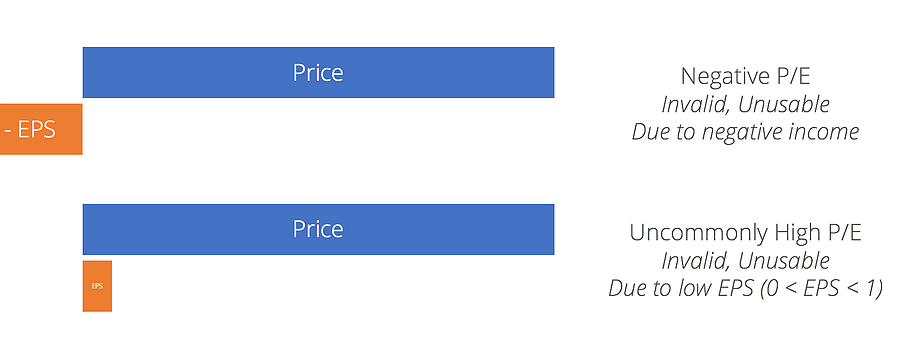
Additional Resources
Cheers for reading CFI'due south guide to Price Earnings Ratio. To continue learning and advancing your career, these additional resource will be helpful:
- Financial Modeling Guide
- Income Argument Template
- Residuum Sail
- PEG Ratio
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/valuation/price-earnings-ratio/
0 Response to "Can a Company's Shares Exhibit a Negative P/e Ratio"
Post a Comment